Self-hosted Runners#
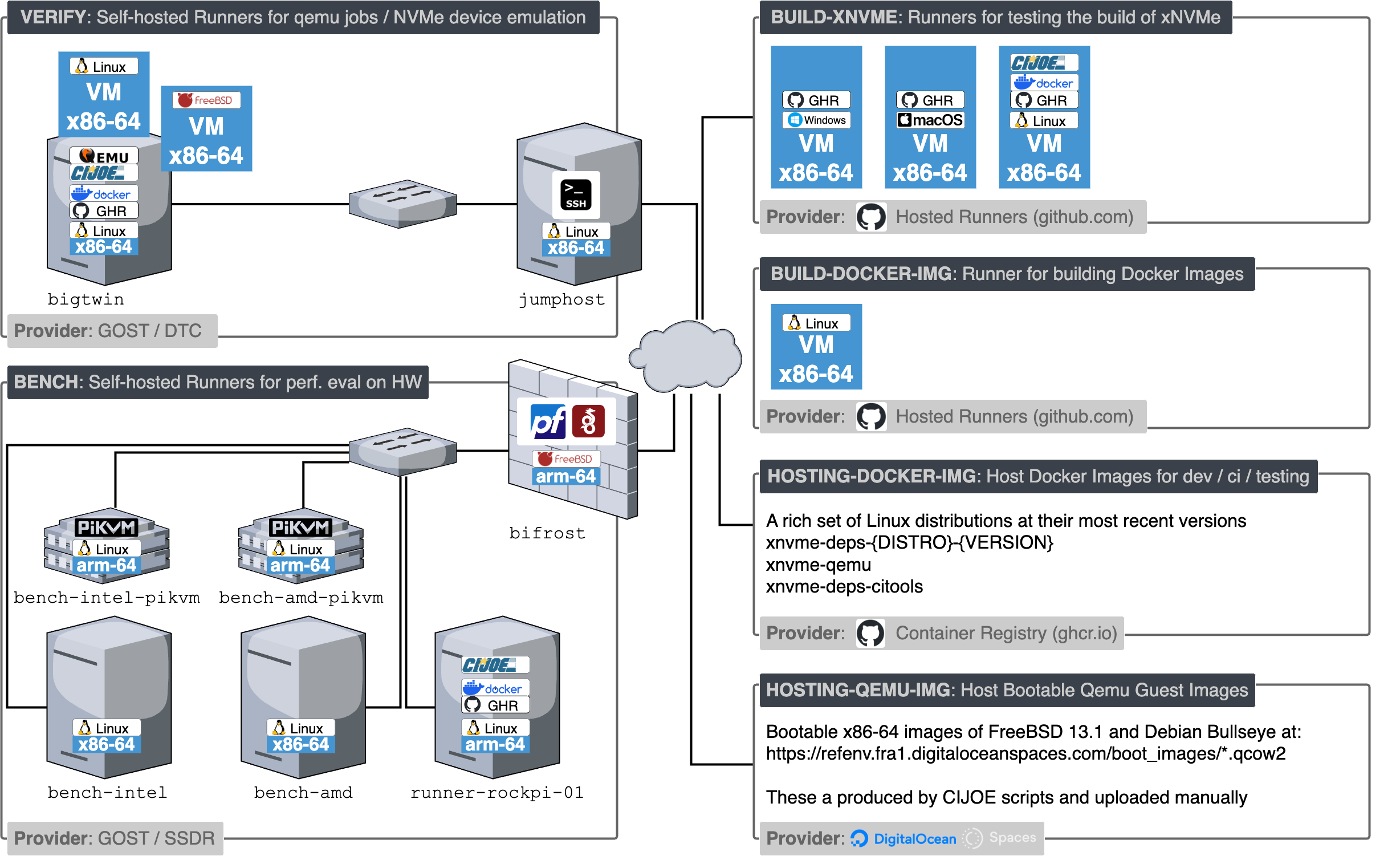
xNVMe CI environments and resources#
The physical hardware resources utilized in the xNVMe CI reside in an isolated network, which is only accessible via a WireGuard VPN. This section will present the hardware in the network responsible for access and GHA runners, and describe the setup of it.
System Notes#
bifrost#
Taking care of the firewall and VPN tasks is a Netgate 1100 running pfSense+ with the following setup:
Firewall rules: default to deny
DHCP Server with mac-address based IP assignment
WireGuard Enabled
See the Netgate 1100 Manual for details on how to configures this.
pixie#
The self-hosted runners for the GitHub Actions are run on a single machine,
pixie, which distributes the work between the machines in the xNVMe CI
environment. This is a HardKernel ODROID running Debian Bookworm.
CPU |
Memory |
Motherboard |
NVMe Devices |
|---|---|---|---|
Intel Pentium Silver N6005 @ 2.00GHz |
16GB SODIMM Synchronous 2667 MT/s |
HARDKERNEL ODROID-H3 |
|
Setup#
Add a user for the github action runner, named ghr:
adduser ghr
usermod -aG sudo ghr
Install some tools:
apt-get -qy install \
git \
vim \
time \
tree
Configure the NVMe storage, by doing the following:
Partition and ext4-format
fdisk /dev/nvme0n1
mkfs.ext4 /dev/nvme0n1p1
Get the UUID
Run:
blkid
Edit
/etc/fstabusing the UUID with mount-point at/gha
Then reload:
systemctl daemon-reload
mount /ghr
chown -R ghr:ghr /ghr
Installing docker#
Do this:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
sh ./get-docker.sh
Change docker to store container-images and temporary data onto the NVMe device, to avoid wear on the emmc:
# Setup a docker config
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d
echo "[Service]" >> /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/docker.conf
echo "ExecStart=" >> "/etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/docker.conf"
echo "ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd --data-root /ghr/docker" >> "/etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/docker.conf"
# Reload it
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
GitHub Actions Runners#
Switch to the ghr user, go into the /ghr mountpoint.
su ghr
cd /ghr
Download and extract the github-action-runner by following the guide on GitHub. This can be found by going to the repository settings, then go to “Actions” and “Runners”. When clicking the “Add ned self-hosted runner” button, run the commands under “Download”.
To create the six runners we need, define the following variables. The token can be found on the page for adding new self-hosted runners under the “Configure” header.
export RUNNERS="bench-intel perf-lat-fbsd perf-lat-linux perf-lat-win verify-macos verify-debian"
export RUNNER_USER=ghr
export URL=https://github.com/xnvme/xnvme
export TOKEN={SUPER_SECRET}
With the above defined, the following commands will configure the six runners:
cd /ghr
# Setup runners
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do cp -r actions-runner "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; done;
# Register runners
cd /ghr/runner-for-bench-intel
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,Linux,X64,intel,bench --replace --name runner-for-bench-intel
cd /ghr/runner-for-perf-lat-fbsd
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,X64,perf-lat,perf-lat-fbsd --replace --name runner-for-perf-lat-fbsd
cd /ghr/runner-for-perf-lat-linux
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,X64,perf-lat,perf-lat-linux --replace --name runner-for-perf-lat-linux
cd /ghr/runner-for-perf-lat-win
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,X64,perf-lat,perf-lat-win --replace --name runner-for-perf-lat-win
cd /ghr/runner-for-verify-debian
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,Linux,X64,amd,verify,Debian --replace --name runner-for-verify-debian
cd /ghr/runner-for-verify-macos
./config.sh --unattended --url ${URL} --token ${TOKEN} --no-default-labels --labels self-hosted,ARM64,verify,macOS --replace --name runner-for-verify-macos
Install and run the runners as services with the following commands:
cd /ghr
# Service(s): install
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; sudo ./svc.sh install ${RUNNER_USER}; popd; done
# Service(s): start
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; sudo ./svc.sh start; popd; done
# Service(s): status
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; sudo ./svc.sh status; popd; done
When needing to update the runners, run the following commands:
# Services: stop
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; sudo ./svc.sh stop; popd; done
# Services: uninstall
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; sudo ./svc.sh uninstall; popd; done
# Remove the runner
for RUNNER_NAME in $RUNNERS; do pushd "runner-for-${RUNNER_NAME}"; ./config.sh remove --token ${TOKEN}; popd; done;